Hair loss can be a tough problem for many people. It can make them feel less confident. But there’s good news. Hair transplants offer a way to get hair back.
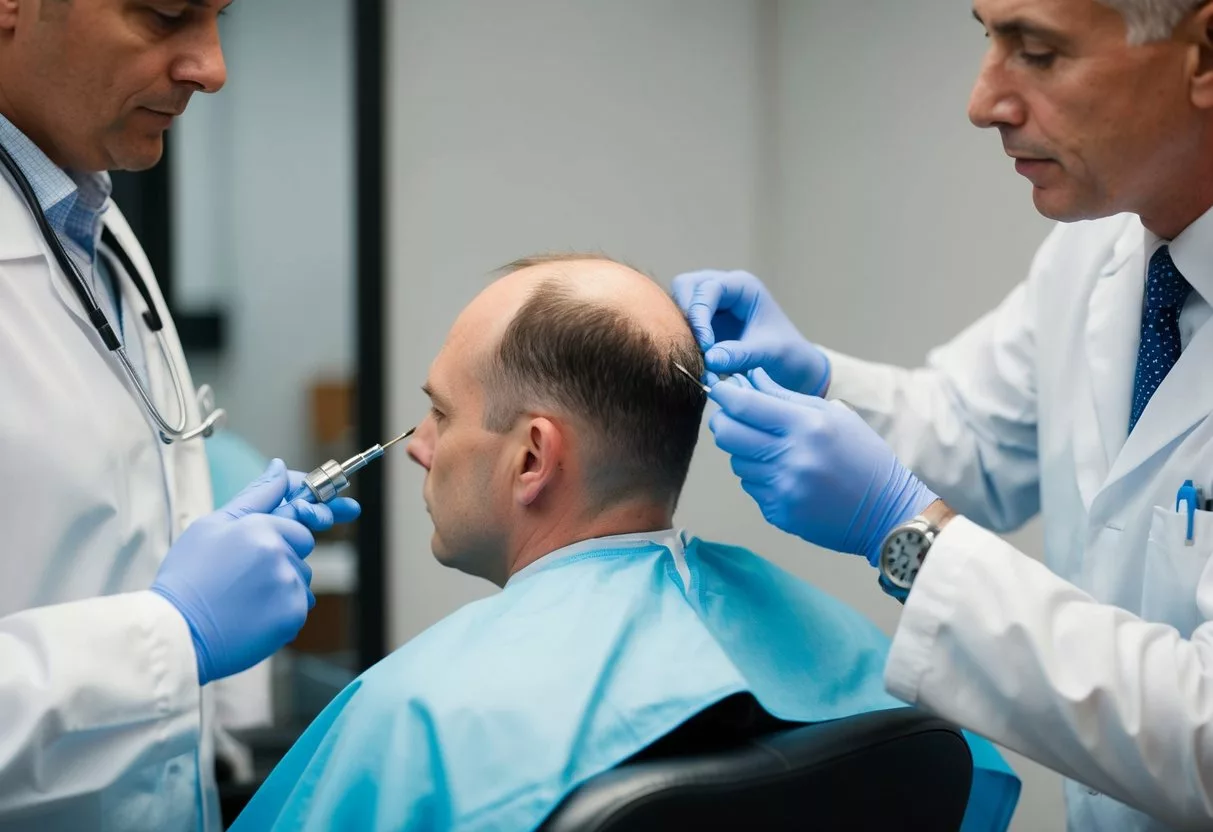
A hair transplant moves hair from one part of the head to another. It takes hair from areas with more growth and puts it where it’s thinning. This helps create a fuller look. Hair transplant surgery can work for both men and women.
There are two main types of hair transplants. One is called FUT, which takes a strip of skin with hair. The other is FUE, which takes out single hair follicles. Both can give good results. A hair loss expert can help pick the best choice for each person.
Understanding Hair Loss
Hair loss affects millions of people worldwide. It can happen for many reasons and impact both men and women. Knowing why hair falls out helps in finding the right treatment.
Causes of Hair Loss
Hair loss can stem from various factors. Genes play a big role, but other things matter too.
Diet, stress, and some health issues can lead to thinning hair. Certain meds may also cause hair to fall out.
Hormonal changes, like those during pregnancy or menopause, can affect hair growth. Age is another key factor, as hair naturally thins over time.
Harsh hair treatments and tight hairstyles can damage hair follicles. This may lead to hair loss if done often.
Androgenetic Alopecia
Androgenetic alopecia is the most common type of hair loss. It’s also known as male or female pattern baldness.
In men, hair often starts to thin at the temples and crown. Women may see thinning all over the scalp.
This type of hair loss is linked to genes and hormones. It tends to run in families.
Hair follicles shrink over time, leading to shorter, finer hairs. Eventually, some follicles stop producing hair.
Non-Genetic Factors
Not all hair loss comes from genes. Many other things can cause thinning hair.
Stress can trigger a type of hair loss called telogen effluvium. This often happens after a big life change or illness.
Poor nutrition, especially low iron or protein, can lead to hair loss. Eating a balanced diet helps keep hair healthy.
Some health issues like thyroid problems or autoimmune diseases can cause hair to fall out. Treating these conditions often helps hair grow back.
Certain meds, like those for cancer or arthritis, may cause hair loss as a side effect. Hair usually grows back when the treatment ends.
Fundamentals of Hair Transplant
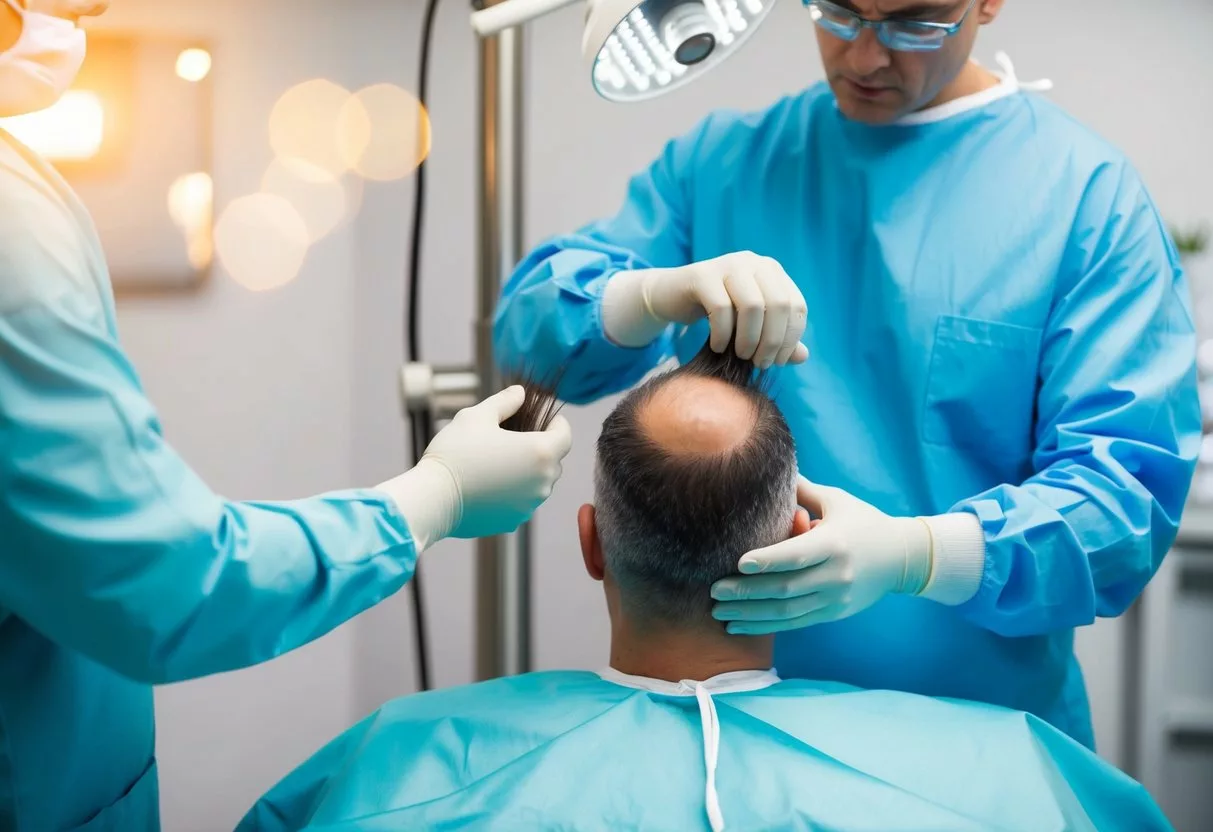
Hair transplant surgery is a procedure that moves hair from one area of the scalp to another. It aims to restore hair growth in areas with thinning or no hair. The process uses existing hair follicles to create a fuller, more natural-looking head of hair.
What Is Hair Transplant Surgery
Hair transplant surgery is a medical procedure that takes hair from areas with thicker growth and moves it to balding or thinning areas. The surgeon removes small pieces of scalp with hair follicles from the donor site, usually the back of the head.
These pieces are then transplanted to the recipient site. The transplanted hair falls out within a few weeks, but new growth starts in a few months. Full results typically appear after 6-12 months.
The procedure is done under local anesthesia. It can take several hours, depending on the size of the transplant. Most patients can return home the same day.
Hair Transplant Techniques
There are two main hair transplant techniques: Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT) and Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE).
FUT involves removing a strip of scalp from the donor area. The surgeon then divides this strip into tiny grafts, each containing one to four hairs. These grafts are planted in the recipient area.
FUE removes individual hair follicles directly from the scalp. The surgeon makes tiny punctures to extract the follicles. These are then transplanted to the balding areas.
Both techniques have pros and cons. FUT can move more grafts in one session. FUE leaves less scarring but takes longer to perform. The choice depends on the patient’s needs and the surgeon’s recommendation.
Preparation for Hair Transplant
Getting ready for a hair transplant involves important steps. Proper preparation helps ensure the best outcome and reduces risks.
Initial Consultation
The first step is meeting with a hair transplant surgeon. During this visit, the doctor will check your scalp and hair loss pattern. They’ll ask about your medical history and any medications you take.
The surgeon will explain different hair transplant techniques and help you choose the best option. They’ll also discuss expected results and possible risks.
Bring a list of questions to ask. Topics to cover include the surgeon’s experience, cost, and recovery time. Ask about before and after photos of past patients.
Pre-Surgery Instructions
Following the doctor’s instructions before surgery is crucial. They may ask you to stop certain medications that can increase bleeding risk. This often includes aspirin and some herbal supplements.
Patients should quit smoking at least two weeks before the procedure. Smoking can slow healing and affect results. The doctor may also advise changes to your diet and alcohol intake.
On the day of surgery, wear loose, comfortable clothing. Don’t use hair products or style your hair. Arrange for someone to drive you home after the procedure.
Your doctor will give you specific instructions on washing your hair before surgery. Follow these carefully to reduce the risk of infection.
Hair Transplant Techniques Explored
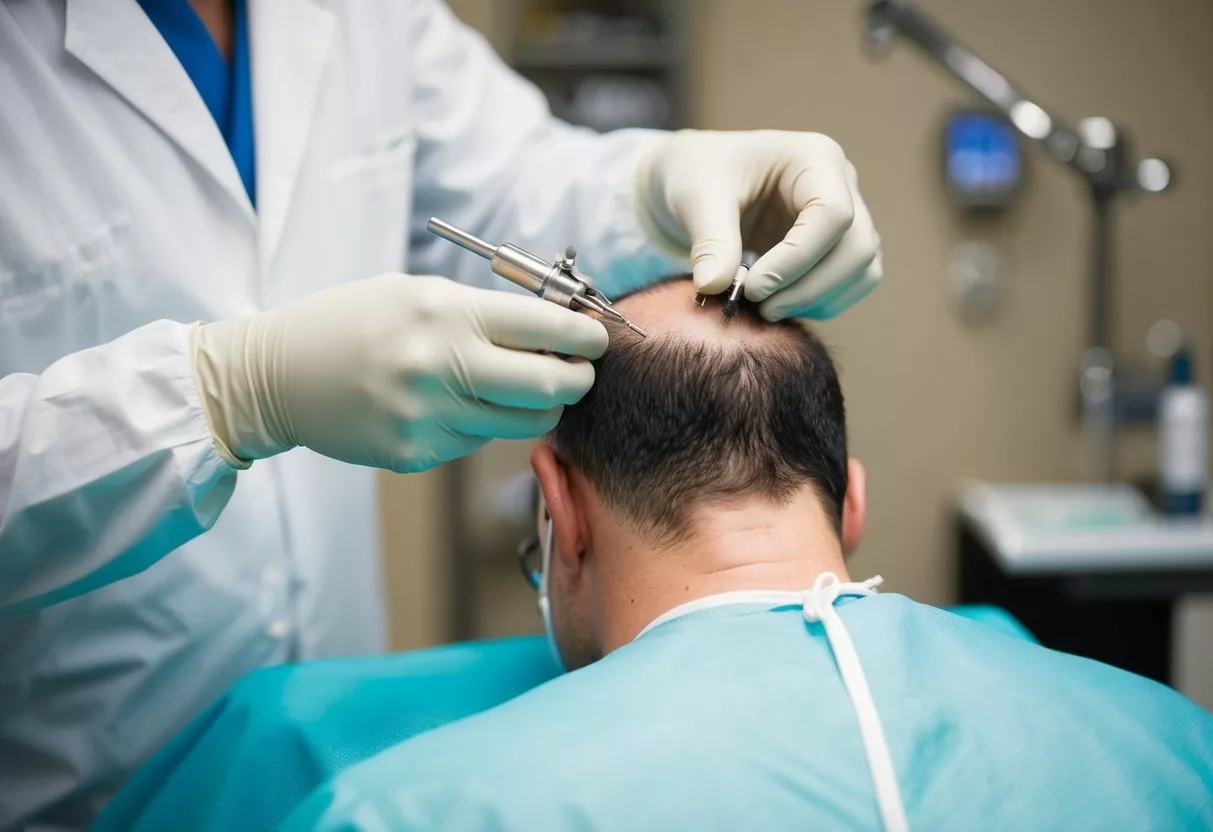
Hair transplant techniques have evolved to offer effective solutions for hair restoration. The main methods focus on moving hair follicles from areas with thick growth to balding or thinning regions.
Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE)
FUE is a popular hair transplant method. It involves removing individual hair follicles from the donor area. The surgeon uses a small punch tool to extract the follicles.
FUE leaves tiny dot scars that are hard to see. This technique works well for people who want to wear very short hairstyles. The recovery time is usually quick.
Key benefits of FUE:
- Minimal scarring
- Natural-looking results
- Faster healing
Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT)
FUT, also known as strip surgery, is another common technique. The surgeon removes a strip of skin with hair from the back of the head. They then divide it into tiny grafts.
This method can move a large number of grafts in one session. It may leave a linear scar, but skilled surgeons can make it very thin. FUT is often a good choice for those needing extensive coverage.
FUT advantages:
- Allows for more grafts in one session
- Can be more cost-effective
- Good for larger balding areas
Other Grafting Methods
Several other grafting techniques exist. Micrografts use very small grafts with just 1-2 hair follicles. This creates a natural hairline.
DHI (Direct Hair Implantation) is a newer method. It uses a special tool to implant hair directly into the scalp. This can give more control over hair direction and density.
Some doctors combine methods for best results. The choice depends on the patient’s needs, hair type, and the extent of hair loss.
Procedure of Hair Transplant
Hair transplant surgery involves moving hair follicles from one area to another. The process has three main steps that work together to create natural-looking results.
Donor Site Harvesting
The surgeon starts by giving local anesthesia to numb the scalp. They then remove hair from the donor site, usually the back or sides of the head. There are two main methods:
- Strip harvesting: The doctor cuts out a strip of scalp and stitches the area closed.
- Follicular unit extraction (FUE): Individual follicles are removed using a special tool.
FUE leaves tiny dots that heal quickly. Strip harvesting leaves a thin scar. The choice depends on the patient’s needs and the surgeon’s recommendation.
Graft Preparation
After harvesting, the team prepares the grafts. They separate the removed hair into tiny units of 1-4 hairs each. These are called follicular unit grafts.
The grafts are kept in a special solution to keep them healthy. The team carefully inspects each graft to ensure it’s viable for transplant.
This step is crucial for creating a natural look. It requires skill and patience to handle the delicate hair follicles properly.
Graft Placement
The final step is placing the grafts in the recipient site. The surgeon makes tiny holes or slits in the balding area.
They carefully place each graft into these holes. The angle and direction of placement are crucial. They must match the surrounding hair for a natural look.
The surgeon places smaller grafts at the front of the hairline. Larger grafts go behind for a fuller look. This process can take several hours, depending on the number of grafts.
After placement, the scalp is bandaged. The transplanted hair will fall out in a few weeks, but new growth should start in 3-4 months.
Postoperative Care and Recovery
Proper care after a hair transplant is crucial for optimal results. Following specific guidelines helps ensure a smooth healing process and promotes successful hair growth.
Immediate Postoperative Care
After the procedure, the scalp needs special attention. The doctor will apply a bandage to protect the transplanted area. This stays on for 1-2 days. Patients may feel discomfort and see some swelling.
Pain medication helps manage any pain. The doctor might prescribe antibiotics to prevent infection. It’s important to keep the head elevated while sleeping to reduce swelling.
Patients should avoid touching or scratching the scalp. This helps prevent irritation and protects new grafts.
Home Care Instructions
Once home, gentle care is key. Patients should wash their hair carefully following their doctor’s instructions. This usually starts 2-3 days after surgery.
Use mild shampoo and lukewarm water. Gently pat the scalp dry – don’t rub. Avoid direct sunlight on the scalp for the first month.
Don’t use hair products or wear hats for the first week. Avoid strenuous activities for at least two weeks. This includes heavy lifting and intense exercise.
Watch for signs of infection like fever or unusual pain. Contact the doctor if these occur.
Expected Recovery Timeline
The first week after surgery is crucial. Scabs may form around transplanted follicles. These fall off naturally within 7-10 days.
Weeks 2-4 often bring temporary shedding of transplanted hair. This is normal and not a cause for alarm.
By month 3, new hair growth usually begins. Full results typically appear 9-12 months after the procedure.
Patients may notice some redness or folliculitis in the first few months. These issues usually resolve on their own.
Regular check-ups with the doctor help monitor progress. Following aftercare instructions closely improves chances of successful hair growth.
Potential Risks and Complications
Hair transplant surgery is generally safe, but it can have some risks and side effects. Patients should be aware of possible complications and take steps to reduce their chances of occurring.
Understanding the Risks
Hair transplant surgery may lead to bleeding, infection, or swelling of the scalp. These issues usually clear up within a few weeks. Some patients experience itching or discomfort after the procedure.
Scarring is another possible outcome. Stretch-back scars may form due to tension from scalp reduction procedures. Keloid scars, which are raised and enlarged, can also develop in rare cases.
Shock loss is a temporary shedding of existing hair near the transplant area. This typically resolves on its own. Numbness in the treated areas may occur but often improves over time.
Folliculitis, an inflammation of hair follicles, can happen after surgery. In some instances, not all transplanted grafts will “take” or grow successfully.
Minimizing Complications
Choosing a skilled and experienced surgeon is crucial for reducing risks. Patients should follow all pre- and post-operative instructions carefully.
Proper wound care helps prevent infections. Keeping the scalp clean and avoiding scratching can lower the risk of complications like folliculitis.
Patients should avoid strenuous activities and protect their scalp from sun exposure after surgery. This helps minimize bleeding and promotes proper healing.
Taking prescribed medications as directed can help manage pain and reduce the risk of infection. Patients should report any unusual symptoms to their doctor promptly.
Avoiding smoking and limiting alcohol intake before and after surgery can improve healing and reduce complications. A healthy diet and staying hydrated also support recovery.
Outcomes and Considerations
Hair transplants can provide significant improvements for many people with hair loss. Results vary based on individual factors and the specific technique used.
Immediate vs. Long-Term Results
Right after a hair transplant, the transplanted area may look swollen and red. This is normal and usually subsides within a few days. The transplanted hair often falls out within 2-3 weeks. This is part of the process.
New hair growth typically starts 3-4 months after the procedure. Full results can take 9-12 months to develop. The transplanted hair follicles continue to grow hair over time, just like natural hair.
For many patients, hair regrowth in the treated areas is 85-90% successful. The new hair blends with existing hair to create a fuller look.
Realistic Expectations
Hair transplants can improve hair density in bald areas or receding hairlines. But they cannot stop future hair loss in non-transplanted areas.
Patients should have enough healthy donor hair to cover the balding areas. The amount of coverage possible depends on:
- Hair characteristics (color, texture, curl)
- Size of the bald area
- Amount of available donor hair
Some patients may need multiple procedures to achieve desired results. Ongoing treatments like minoxidil or finasteride may help maintain results long-term.
Hair transplants do not create new hair follicles. They redistribute existing hair to areas with thinning or no hair. This limits how much hair density can be achieved.
Supportive Treatments and Alternatives
Hair transplants aren’t the only option for treating hair loss. There are many other treatments that can help. Some are medicines you take, while others use new technologies.
Medications and Non-Surgical Options
Minoxidil, also known as Rogaine, is a common treatment. You put it on your scalp to slow hair loss and help new hair grow. It works for both men and women.
Finasteride, sold as Propecia, is a pill for men. It stops testosterone from turning into DHT, which causes hair loss. Many men see good results with this medicine.
Saw palmetto is a natural option some people try. It may help block DHT like finasteride does.
For thinning eyebrows, special serums can help. These often contain peptides and vitamins to make brows fuller.
Advanced Therapies
Low-level laser therapy uses special light to boost hair growth. You can get this done at a clinic or use a laser cap at home.
Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) injections use your own blood to help hair grow. A doctor takes some of your blood, spins it to get the good parts, then injects it into your scalp.
Scalp micropigmentation is like a hair tattoo. It doesn’t make hair grow, but it can make thinning hair look fuller.
Costs and Insurance
Hair transplant costs vary widely and are rarely covered by insurance. Understanding the financial aspects is crucial for those considering this procedure.
Evaluating Hair Transplant Costs
Hair transplants typically cost between $4,000 and $15,000. The price depends on factors like the number of grafts needed and the surgeon’s expertise. Some high-end clinics may charge up to $25,000 for a procedure.
Pricing is often based on grafts. Each graft usually costs $2 to $10. A full transplant might require thousands of grafts.
Location affects cost. Clinics in big cities or areas with a high cost of living often charge more.
The surgeon’s experience and reputation also impact the price. Well-known experts may charge premium rates.
Insurance and Financing
Most insurance plans don’t cover hair transplants. They’re considered cosmetic procedures, not medical necessities.
Some clinics offer financing options. These may include payment plans or medical credit cards.
Patients can explore personal loans or health savings accounts (HSAs) to fund their procedures.
It’s important to get a detailed cost breakdown before committing. This should include all fees, not just the surgery itself.
Some clinics offer package deals for multiple sessions. These can be more cost-effective for extensive transplants.
Frequently Asked Questions
Hair transplant procedures involve various steps and considerations. Patients often have questions about what to expect, potential side effects, and recovery times.
What can be expected before and after a hair transplant procedure?
Before a hair transplant, patients undergo a consultation to assess their hair loss and determine the best approach. The surgeon may recommend stopping certain medications temporarily.
After the procedure, patients can expect some swelling and discomfort in the treated areas. The transplanted hair will fall out within a few weeks, which is normal. New hair growth typically begins in 3-4 months.
What are common side effects associated with hair transplants?
Common side effects include temporary swelling, bruising, and numbness in the treated areas. Some patients may experience itching or minor infections at the transplant sites.
Scarring is possible but usually minimal with modern techniques. In rare cases, shock loss of existing hair may occur, but this is typically temporary.
How does a hair transplant procedure work?
Hair transplants involve moving hair from areas of thicker growth to balding or thinning areas. The surgeon removes hair follicles from the donor site, usually the back of the head.
These follicles are then carefully transplanted to the recipient areas. The procedure can take several hours depending on the extent of hair loss and transplantation needed.
What is the average recovery time for a hair transplant?
Most patients can return to work within 3-5 days after the procedure. The transplanted area may be sensitive for a few weeks.
Full recovery, including the shedding of transplanted hair and new growth, takes several months. Final results are typically visible after 6-12 months.
What are the success rates of hair transplant surgeries?
Success rates for hair transplants are generally high when performed by experienced surgeons. Most patients see significant improvement in hair density and coverage.
Individual results can vary based on factors like the extent of hair loss, donor hair quality, and adherence to post-operative care instructions.
Is there significant pain associated with hair transplant procedures?
Hair transplant procedures are typically performed under local anesthesia. This helps minimize pain during the surgery. Patients may feel some pressure or discomfort.
Post-procedure pain is usually mild. It can be managed with over-the-counter pain medication. Most patients report minimal discomfort during recovery.