St. John’s Wort, also known as Hypericum perforatum, is a flowering plant that has been used for centuries as a medicinal herb. The plant is native to Europe but has since been introduced to other parts of the world, including North America. St. John’s Wort has been used to treat a variety of ailments, including depression, anxiety, and sleep disorders.
Historically, St. John’s Wort has been used to treat a range of mental health conditions. The ancient Greeks and Romans used it to treat nervous disorders, and it was also used during the Middle Ages to treat melancholy and other mental health conditions. Today, St. John’s Wort is one of the most commonly used herbal supplements in the United States, with millions of people using it to treat depression and other mental health conditions.
Key Takeaways
- St. John’s Wort is a flowering plant that has been used for centuries as a medicinal herb.
- Historically, St. John’s Wort has been used to treat a range of mental health conditions.
- Today, St. John’s Wort is one of the most commonly used herbal supplements in the United States, with millions of people using it to treat depression and other mental health conditions.
Historical Context

St. John’s Wort, also known as Hypericum perforatum, has been used for medicinal purposes for centuries. The plant has a long history of traditional use, dating back to ancient Greece and Rome.
Traditional Uses
St. John’s Wort was traditionally used to treat a wide range of ailments, including wounds, burns, and nervous disorders. The plant was also believed to have magical powers and was used to ward off evil and protect against disease. In medieval times, St. John’s Wort was used to treat depression and anxiety, and it is still commonly used for this purpose today.
Etymology and Nomenclature
The name St. John’s Wort comes from the plant’s association with St. John the Baptist, whose feast day falls on June 24th, around the time when the plant is in full bloom. The plant has also been known by other names throughout history, including Klamath weed, goatweed, and tipton weed.
In conclusion, St. John’s Wort has a rich history of traditional use and has been valued for its medicinal properties for centuries. Its use continues to be popular today, particularly for the treatment of depression and anxiety.
Botanical Description
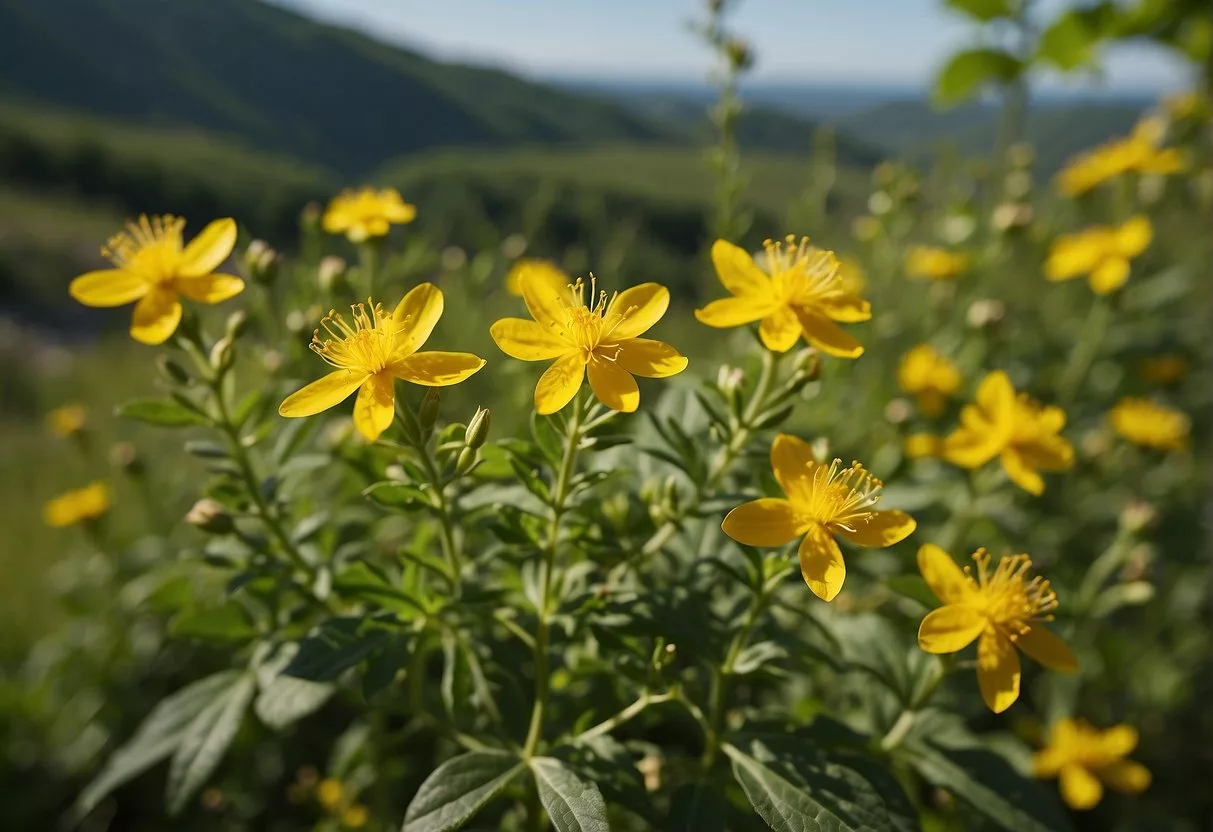

Plant Characteristics
St. John’s Wort (Hypericum perforatum) is a herbaceous perennial plant that belongs to the Hypericaceae family. It is native to Europe, western Asia, and northern Africa but has been naturalized in many parts of the world. The plant can grow up to one meter tall and has many branches. The leaves are opposite, oblong, and about 1-2 cm long. The flowers are bright yellow and have five petals, five sepals, and numerous stamens. The plant blooms from June to September.
Active Compounds
St. John’s Wort is known for its active compounds, including hypericin, hyperforin, and flavonoids. Hypericin is a red pigment found in the plant’s flowers, leaves, and stems. It is known for its antidepressant and antiviral properties. Hyperforin is a phloroglucinol derivative found in the plant’s leaves and flowers. It has been shown to have antidepressant, anxiolytic, and anti-inflammatory properties. Flavonoids are a group of plant pigments that have antioxidant properties. St. John’s Wort is rich in flavonoids, including quercetin, kaempferol, and rutin.
St. John’s Wort has been used for centuries as a traditional medicine to treat various ailments, including depression, anxiety, and nerve pain. It is available in many forms, including capsules, tablets, and teas. However, it is important to note that St. John’s Wort can interact with many prescription medications, including antidepressants, birth control pills, and blood thinners. Therefore, it is important to consult a healthcare professional before using St. John’s Wort as a supplement.
Medical Uses

St. John’s Wort has been used for centuries to treat a variety of conditions. In recent years, it has gained popularity as a natural remedy for mood disorders, skin conditions, and other therapeutic effects.
Mood Disorders
Several studies have shown that St. John’s Wort can be an effective treatment for mild to moderate depression. It is believed to work by increasing the levels of serotonin, dopamine, and norepinephrine in the brain. These neurotransmitters are responsible for regulating mood, and increasing their levels can help alleviate symptoms of depression. However, it is important to note that St. John’s Wort should not be used to treat severe depression, as it may not be effective and could interact with other medications.
Skin Conditions
St. John’s Wort has also been used to treat a variety of skin conditions, including wounds, burns, and eczema. It is believed to have anti-inflammatory and antibacterial properties, which can help speed up the healing process. Some studies have also suggested that St. John’s Wort may be effective in treating psoriasis, a chronic skin condition characterized by itchy, scaly patches.
Other Therapeutic Effects
St. John’s Wort has been used to treat a variety of other conditions, including PMS, menopause, and inflammation. Some studies have suggested that it may be effective in reducing the severity of menopausal symptoms, such as hot flashes and mood swings. Additionally, St. John’s Wort has been shown to have anti-inflammatory properties, which may make it useful in treating conditions such as arthritis and other inflammatory disorders.
It is important to note that St. John’s Wort can interact with other medications, including antidepressants, and should not be taken without consulting a healthcare professional. Additionally, it may cause side effects such as dry mouth, dizziness, and gastrointestinal symptoms. As with any supplement or medication, it is important to use St. John’s Wort only as directed and under the guidance of a healthcare professional.
Pharmacology

St. John’s Wort (SJW) has been shown to have a complex pharmacology with multiple mechanisms of action. The main active constituents of SJW are hyperforin and hypericin, which are believed to be responsible for its antidepressant effects.
Mechanism of Action
SJW has been shown to inhibit the reuptake of serotonin, dopamine, and norepinephrine, leading to an increase in the concentration of these neurotransmitters in the synaptic cleft. This effect is similar to that of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), which are commonly used antidepressants. SJW has also been shown to modulate the activity of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) and glutamate receptors, which may contribute to its anxiolytic effects.
Neurotransmitter Effects
The increase in serotonin levels caused by SJW is thought to be responsible for its antidepressant effects. Serotonin is a neurotransmitter that regulates mood, appetite, and sleep. Low levels of serotonin have been linked to depression and anxiety disorders. The increase in dopamine and norepinephrine levels caused by SJW may also contribute to its antidepressant effects. Dopamine is a neurotransmitter that is involved in reward processing and motivation, while norepinephrine is involved in the stress response.
In conclusion, SJW has a complex pharmacology with multiple mechanisms of action. It has been shown to inhibit the reuptake of serotonin, dopamine, and norepinephrine, leading to an increase in the concentration of these neurotransmitters in the synaptic cleft. SJW has also been shown to modulate the activity of GABA and glutamate receptors, which may contribute to its anxiolytic effects. The increase in serotonin levels caused by SJW is thought to be responsible for its antidepressant effects.
Administration and Dosage

Forms of Consumption
St. John’s Wort is available in various forms of consumption, including capsules, tea, tincture, and oil. Capsules are the most common form of consumption as they are easy to take and have a standardized dosage. Tea can be made by steeping the dried flowers in hot water for a few minutes. Tincture is a concentrated liquid extract that can be added to water or juice. Oil can be applied topically to the skin.
Recommended Dosage
The recommended dosage of St. John’s Wort varies depending on the form of consumption. In most clinical studies, the usual adult dosage was 300 mg taken three times daily with food, for a total of 900 mg of St. John’s Wort per day [1]. It is important to make sure that the product has a standardized amount of hypericin, one of the active compounds in St. John’s Wort.
For tea, one to two teaspoons of dried flowers can be steeped in hot water for 10 to 15 minutes, up to three times a day. Tincture can be taken in a dose of 2 to 4 mL, up to three times a day. Oil can be applied topically to the skin as needed.
It is important to note that the dosage of St. John’s Wort should not exceed the recommended daily dose as it may cause adverse effects. Additionally, St. John’s Wort may interact with certain medications, including antidepressants, birth control pills, and blood thinners. Therefore, it is recommended to consult with a healthcare provider before taking St. John’s Wort.
[1] St. John’s Wort Dosage Guide – GoodRx
Drug Interactions and Contraindications

St. John’s Wort is a popular herbal supplement that is used to treat mild to moderate depression. However, it is important to note that it can interact with other medications and cause unwanted side effects. In this section, we will discuss some of the prescription medications, birth control, and pregnancy, and specific drug examples that can interact with St. John’s Wort.
Prescription Medications
St. John’s Wort can interact with several prescription medications, including warfarin, digoxin, cyclosporine, and statins. These medications are used to treat a variety of conditions, including blood clots, heart failure, and high cholesterol. St. John’s Wort can make these medications less effective, which can lead to serious health problems. Therefore, it is important to talk to a healthcare provider before taking St. John’s Wort if you are already taking any of these medications.
Birth Control and Pregnancy
St. John’s Wort can also interact with birth control pills and other forms of hormonal contraception. It can make these medications less effective, which can increase the risk of pregnancy. Therefore, it is important to use an additional form of contraception if you are taking St. John’s Wort. Additionally, St. John’s Wort should not be taken during pregnancy or while breastfeeding, as it can have harmful effects on the developing fetus or infant.
Specific Drug Examples
Some specific examples of medications that can interact with St. John’s Wort include antidepressants, such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) and monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs). St. John’s Wort can increase the risk of serotonin syndrome, a potentially life-threatening condition that can cause symptoms such as agitation, confusion, and seizures. Therefore, it is important to talk to a healthcare provider before taking St. John’s Wort if you are already taking an antidepressant.
In conclusion, St. John’s Wort can interact with several medications and should be used with caution. It is important to talk to a healthcare provider before taking St. John’s Wort if you are already taking any prescription medications or hormonal contraception. Additionally, St. John’s Wort should not be taken during pregnancy or while breastfeeding.
Side Effects and Adverse Reactions
St. John’s Wort is generally considered safe when taken in recommended doses for short periods of time. However, some people may experience side effects or adverse reactions. This section will discuss the most common side effects and serious health risks associated with St. John’s Wort.
Common Side Effects
The most common side effects of St. John’s Wort include dry mouth, dizziness, diarrhea, fatigue, headache, and photosensitivity. These side effects are usually mild and go away on their own after a few days of taking the supplement. However, if these side effects persist or become severe, it is important to contact a healthcare provider.
Serious Health Risks
While St. John’s Wort is generally safe, it can cause serious health risks in some people. One of the most serious risks is serotonin syndrome, a potentially life-threatening condition that occurs when there is too much serotonin in the body. Symptoms of serotonin syndrome include confusion, agitation, hallucinations, rapid heartbeat, high blood pressure, and fever. If you experience any of these symptoms while taking St. John’s Wort, seek medical attention immediately.
St. John’s Wort can also interact with other medications, including antidepressants, birth control pills, and blood thinners. It is important to talk to a healthcare provider before taking St. John’s Wort if you are taking any medications.
In rare cases, St. John’s Wort can cause eye damage, especially if taken in high doses or for long periods of time. It is important to monitor your vision while taking St. John’s Wort and to contact a healthcare provider if you experience any changes in your vision.
Overall, St. John’s Wort is a safe and effective supplement when taken in recommended doses for short periods of time. However, it is important to be aware of the potential side effects and serious health risks associated with this supplement. If you experience any adverse reactions while taking St. John’s Wort, contact a healthcare provider immediately.
Regulatory Status

St. John’s Wort is a popular herbal supplement used for its antidepressant and anxiolytic effects. As with any dietary supplement, the regulatory status of St. John’s Wort is an important consideration for consumers.
FDA Oversight
The FDA does not regulate St. John’s Wort as a drug, but rather as a dietary supplement. This means that St. John’s Wort is not subject to the same rigorous testing and approval process as prescription drugs. However, dietary supplements are still subject to FDA oversight, and manufacturers are required to ensure that their products are safe and accurately labeled.
Consumers should be aware that the FDA does not test dietary supplements for safety or efficacy before they are marketed. Therefore, it is important to purchase St. John’s Wort from a reputable manufacturer and to follow the dosing instructions carefully.
International Regulations
In Europe, St. John’s Wort is regulated as a medicinal product. This means that it is subject to more stringent testing and approval processes than in the United States. In some European countries, St. John’s Wort is available only by prescription.
Consumers should be aware that the regulatory status of St. John’s Wort may vary depending on the country in which they live. It is important to research the regulations in your country before purchasing St. John’s Wort.
Overall, while St. John’s Wort is widely available as a dietary supplement, consumers should be aware of the regulatory status and purchase from reputable manufacturers.
Research and Studies

Clinical Trials
Several clinical trials have been conducted to evaluate the effectiveness of St. John’s Wort in treating depression. In a 26-week clinical trial with 124 participants, St. John’s Wort, a standard antidepressant (sertraline, an SSRI), and a placebo were similarly effective in treating major depression of moderate severity. The study was funded by NCCIH and NIMH. [1] Another study found that St. John’s Wort was superior to placebo in treating mild to moderate depression. [2]
Meta-Analyses
Several meta-analyses of small heterogeneous studies conducted over the past two decades have found St. John’s Wort to be effective in treating mild to moderate depression. [3] However, data regarding the effectiveness of using St. John’s Wort as a stand-alone treatment compared with standard antidepressants has yet to be proven conclusively. [1]
While St. John’s Wort extracts are currently being used to treat depression of various degrees of severity, it is important to note that St. John’s Wort interacts with many drugs and might not be safe for many people, especially those who take conventional medicines. St. John’s Wort can weaken the effects of many medicines, including crucially important medicines such as birth control pills, antidepressants, and blood thinners. [4]
It is recommended that individuals who are considering using St. John’s Wort for depression should consult with a healthcare professional before starting treatment. It is also important to note that St. John’s Wort should not be used as a substitute for conventional medical care or prescription antidepressants. [1]
Considerations for Use

St. John’s Wort is a natural remedy that is widely used to treat depression, anxiety, and other mental health conditions. However, before using this herb, there are some important considerations to keep in mind.
Safety Precautions
St. John’s Wort can interact with other medications and cause adverse effects. For example, it can reduce the effectiveness of birth control pills, leading to unplanned pregnancy. It can also interact with antidepressants, blood thinners, and HIV medications, among others. Therefore, it is essential to consult a healthcare provider before taking St. John’s Wort, especially if you are already taking other medications.
Moreover, St. John’s Wort can cause some side effects, such as dry mouth, dizziness, and gastrointestinal symptoms. In rare cases, it can also cause more severe adverse effects, such as serotonin syndrome, a potentially life-threatening condition that can occur when the herb is taken with other drugs that increase serotonin levels. Therefore, it is crucial to follow the recommended dosage and monitor any side effects that may occur.
Consulting Healthcare Providers
It is essential to consult a healthcare provider before taking St. John’s Wort, especially if you are pregnant or breastfeeding, have a history of mental health conditions, or are taking other medications. A healthcare provider can help you determine if St. John’s Wort is right for you and advise you on the appropriate dosage and potential drug interactions.
In addition, a healthcare provider can monitor your symptoms and adjust your treatment plan as needed. They can also provide you with information on other treatment options, such as counseling or medication, that may be more appropriate for your condition.
Overall, St. John’s Wort can be a useful natural remedy for depression, anxiety, and other mental health conditions. However, it is essential to take safety precautions and consult a healthcare provider before using this herb to ensure that it is safe and effective for you.
Frequently Asked Questions

What are the common uses of St. John’s Wort?
St. John’s Wort has been used to treat mild to moderate depression, anxiety, and sleep disorders. It is also believed to have anti-inflammatory and antiviral properties. However, more research is needed to confirm its effectiveness in treating these conditions.
What are the potential side effects associated with St. John’s Wort?
St. John’s Wort may cause side effects such as dry mouth, dizziness, and gastrointestinal symptoms. It may also cause photosensitivity, which can increase the risk of sunburn and skin damage. Additionally, it can interact with certain medications, including antidepressants, birth control pills, and blood thinners. It is important to speak with a healthcare provider before taking St. John’s Wort.
Can St. John’s Wort interact with other medications?
Yes, St. John’s Wort can interact with other medications, including antidepressants, birth control pills, and blood thinners. It may also interact with certain chemotherapy drugs, immunosuppressants, and HIV medications. It is important to speak with a healthcare provider before taking St. John’s Wort, especially if you are taking any medications.
What is the recommended dosage of St. John’s Wort for treating anxiety?
The recommended dosage of St. John’s Wort for treating anxiety varies depending on the individual and the severity of the anxiety. It is important to speak with a healthcare provider before taking St. John’s Wort for anxiety, as it may interact with other medications and may not be effective for everyone.
Are there any specific groups of people who should avoid taking St. John’s Wort?
St. John’s Wort should not be taken by pregnant or breastfeeding women, as it may be harmful to the baby. It should also not be taken by individuals with bipolar disorder, as it may worsen symptoms. It is important to speak with a healthcare provider before taking St. John’s Wort if you have any medical conditions or are taking any medications.
How does St. John’s Wort affect sleep when taken before bedtime?
St. John’s Wort may have a mild sedative effect and may help improve sleep when taken before bedtime. However, more research is needed to confirm its effectiveness in improving sleep. It is important to speak with a healthcare provider before taking St. John’s Wort for sleep, as it may interact with other medications and may not be effective for everyone.